Authors' Homepages: Anthony Bedford
Wallace Fowler
Chapter 7: Centroids and Centers of Mass
"An object's weight does not act at a single point – it is distributed over the entire volume of the object.
But the weight can be represented by a single equivalent force acting at a point called the center of
mass. When the equilibrium equation are used to determine the reactions exerted on an object by its
supports, the location of the center of mass must be known if the weight of the object is to be included
in the analysis. The dynamic behaviors of objects also depend on the location of their centers of mass.
In this chapter we define the center of mass and show how it is determined for various kinds of objects.
We also introduce definitions that can be interpreted as the average positions of areas, volumes, and
lines. These average positions are called centroids. Centroids coincide with the centers of mass of
particular classes of objects, and they also arise in may other engineering applications."


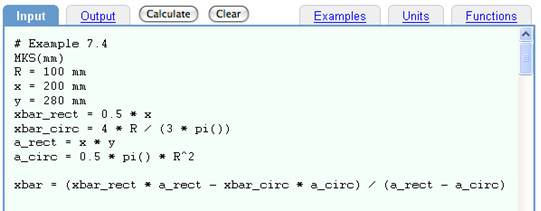
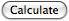 or by typing Shift Enter.
or by typing Shift Enter.