Author's Homepage: R. C. Hibbeler
Chapter 3: Equilibrium of a Particle
"A particle is in equilibrium provided it is at rest if originally at rest or has a constant velocity if originally in motion. Most often, however, the term equilibrium or, more specifically, static equilibrium is used to describe an object at rest. To maintain equilibrium, it is necessary to satisfy Newton’s first law of motion, which requires the resultant force active on a particle to be zero. This condition may be stated mathematically as the sumF = 0 where sumF is the vector sum of all the forces acting on the particle."


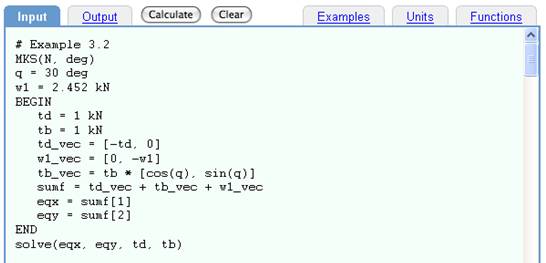
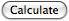 or by typing Shift Enter.
or by typing Shift Enter.