Author's Homepage: Jonathan Wickert
Chapter 7: Motion and Power Transmission
"In this chapter, we turn our attention to the design and operation of
power-transmission equipment as the fifth "element" of mechanical engineering.
Machinery generally comprises gears, shafts, bearings, cams, linkages,
and other building-block components. These mechanism are capable of
transmitting power from one location to another, for instance, from
the engine in an automobile to the drive wheels. Another function
of a mechanism might be to transform one type of motion into another.
An application in that regard, which we encountered in Section 6.6,
is the mechanism for converting the back-and-forth motion of the piston
in an internal-combustion engine into rotational motion of the crankshaft.
The robotic manipulator arms shown in Figures 7.1 and 7.2 are other examples
of mechanisms. Each arm is a chain of interconnected links in which position
is controlled by motors at the joints. Mechanical engineers evaluate the
position, velocity, and acceleration of machines such as these and the
forces and torques that make them move. The analysis and design of
machinery is, in part, an extension of the topics of force systems and
energy systems that we encountered in previous chapters."


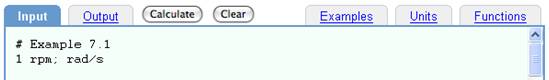
 or by typing Shift Enter.
or by typing Shift Enter.